In industrial manufacturing, the control of emission and air pollutants is a key component in reducing environmental impact while staying compliant with government regulations.
Emission often refers to man-made contaminants, while air pollution can be caused by substances released into the atmosphere as a result of both human activities and natural phenomena.
In addition, air pollution control focuses on gases and particulates that are released into the atmosphere and affect the air quality, while emission control encompasses the abatement of a wider range of pollutants, such as noise and heat, that are released into the environment.
What Is Air Pollution Control?
Air pollution refers to the introduction of toxic chemicals or compounds into the atmosphere that lowers the air quality, harms the environment or human health, and reduces the quality of life (e.g., damaging the ozone layer).
Air pollutants can be created through natural processes (e.g., volcano eruption, microbial decaying process) or generated from manmade sources (e.g., mining, manufacturing processes).
There’s a large number of contaminants that contribute to air pollution – some of them are in gaseous form, while others are in solid form as particulates suspended in the air:
- Sulfur oxides (SOX)
- Nitrogen oxides (NOX)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Carbon dioxide (CO2)
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs)
- Particulate matter
- Mercury in gaseous form
- Radioactive pollutants
- Ammonia
Types of Air Pollution Control
One of the best ways to control air pollution is to switch to cleaner fuels and industrial processes. Otherwise, pollutants need to be collected by air-cleaning devices and discarded appropriately.
Here are some common air pollution control technologies:
- Cyclones
- Scrubbers
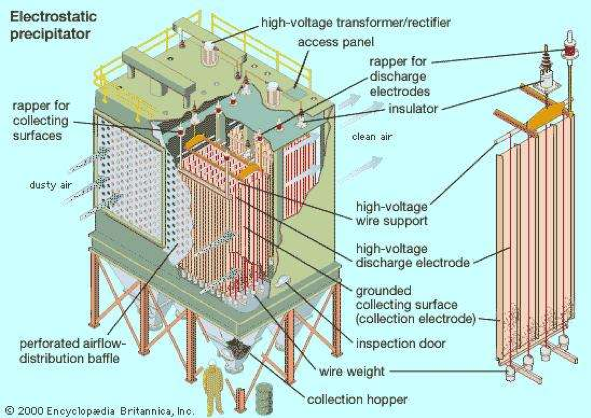
- Electrostatic precipitators
- Baghouse filters
- Absorption
- Wet scrubbers and packed scrubbers
- Flue gas desulfurization
What Is Emission Control?
Emission refers to different types of pollution – such as noise, heat, radiation, and particles – that are discharged into the atmosphere from residential, commercial, and industrial sources.
Emission can come from automobile exhausts, household or commercial cleaning compounds, air conditioning units, power plants, and industrial combustion processes.
Vehicle emission control often involves the abatement of hydrocarbons, carbon monoxide, sulfur oxides, particulate matters, and volatile organic compounds (VOC). Household emissions typically involve greenhouse gases from burning oil or gases for heating, or electricity generated from burning coal, natural gas, or oil. Industrial emission control usually focuses on acid emissions resulting from combustion processes and VOC abatement from manufacturing.
Types of Emission Control
Different strategies and technologies that can be applied to control emissions depending on the nature and sources of the pollutants, such as:
- Catalytic converters for VOC emission control
- Regenerative thermal oxidizer and thermal recuperative oxidizer for VOC abatement
- Rotary concentrator for high air volume low VOC concentration processes
- Particulate filters
- Evaporative emission controls
- Crankcase emission controls
- Thermal management strategies
- Engine and fuel management
- Enhanced combustion technologies
- Sensor technologies
- GHG emissions reduction technologies
- Alternative fuel sources
Emission control is essential in any industrial processes, allowing manufacturers to minimize environmental impact and stay compliant with regulations. Download our free Air Pollution Control Selection Guide to find the right solution.
Sources: